Complete Guide to Diarrhea Causes: Triggers, Types, and Quick Relief
Diarrhea causes range from simple dietary missteps to complex medical conditions, making it a widespread experience that almost everyone encounters at some point. While people often dismiss it as a minor inconvenience, understanding the root diarrhea causes represents the first and most crucial step toward finding effective relief and ruling out serious health issues.
This article explains the most common diarrhea causes, how to recognize warning signs, and evidence-based steps you can take to restore digestive balance safely.
What to Do in the First 24 Hours
Immediate Action Plan for Acute Diarrhea:
- Prioritize oral rehydration solutions (ORS) or water to prevent dehydration
- Start the BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast)
- Rest and allow your body to recover
- Avoid: dairy products, caffeine, fatty foods, alcohol, and high-fiber foods
When to seek immediate medical attention: If you experience fever over 102°F, bloody stools, severe dehydration signs, or symptoms lasting beyond 48 hours.
What Causes Diarrhea? Understanding the Digestive Mechanism
At its core, diarrhea disrupts your digestive system’s delicate balance. It occurs when your intestinal muscles contract too rapidly—a process known as hyperactive peristalsis. Normally, these rhythmic contractions move waste through your gut at a pace that allows optimal fluid and nutrient absorption. However, when this process accelerates, the intestines don’t have enough time to absorb water, which results in the loose, watery stools characteristic of diarrhea.
This abnormal motility forms the central physiological event behind most diarrhea causes, whether acute or chronic. Excessively rapid intestinal movement creates a cascade of digestive disruptions that prevent normal function.
Diarrhea vs. Dysentery: Understanding Key Differences
While both conditions involve bowel urgency and discomfort, distinguishing between them proves critical for proper care. Understanding this difference helps identify the specific diarrhea causes at play.
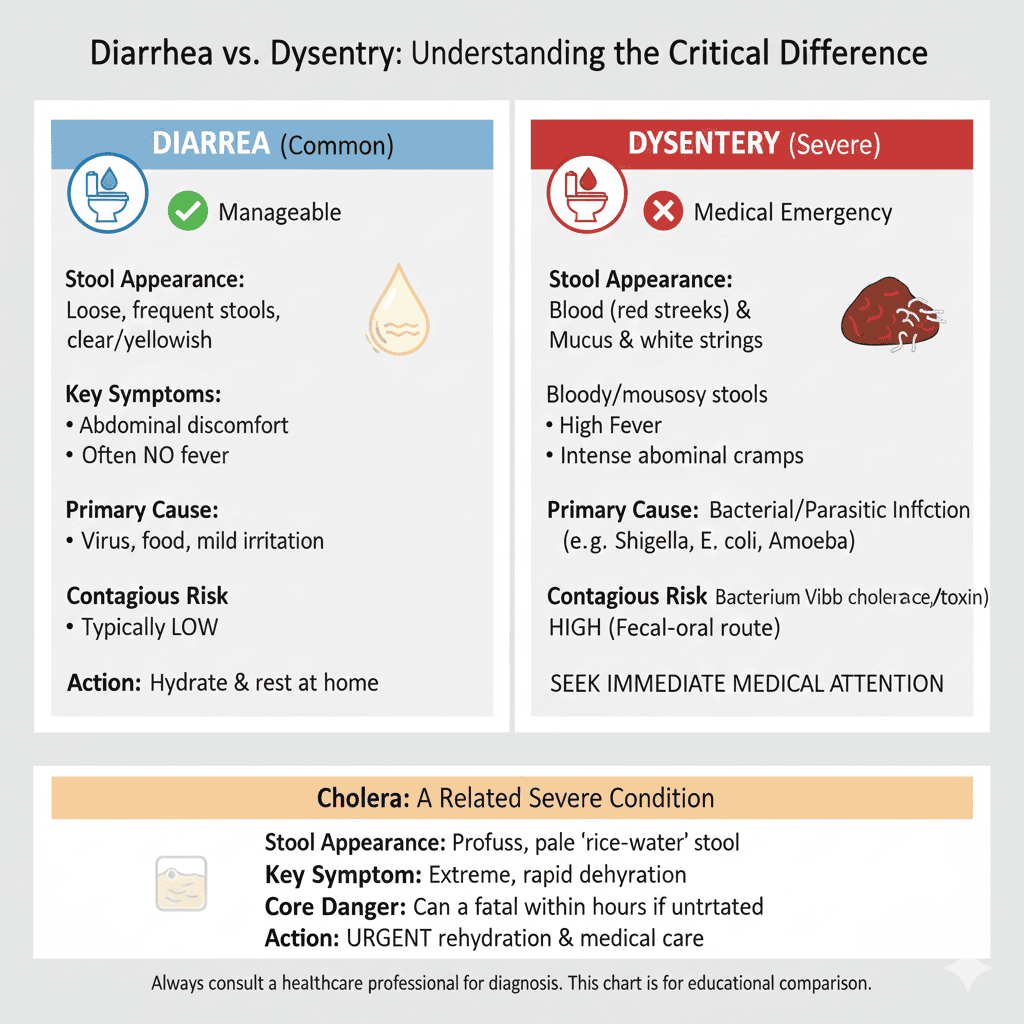
Diarrhea typically does not spread contagiously on its own and often occurs without fever. The stools, while watery, usually consist of the body’s natural waste products expelled too quickly.
Dysentery, on the other hand, represents a severe inflammatory disorder often caused by bacterial or parasitic infections. It frequently spreads contagiously and presents with fever, intense abdominal cramping, and stools containing blood or mucus. This far more serious condition necessitates immediate medical attention.
Another severe condition often confused with general diarrhea is cholera, which has a specific bacterial cause and can lead to life-threatening dehydration rapidly. Research published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases demonstrates how certain bacterial infections create severe secretory diarrhea through toxin production.
Types of Diarrhea Based on Causes
Understanding different diarrhea types helps identify appropriate treatment approaches:
- Acute diarrhea: Sudden onset, typically viral or food-related, lasting less than two weeks
- Chronic diarrhea: Persistent symptoms lasting more than four weeks, often related to IBS, IBD, or celiac disease
- Osmotic diarrhea: Occurs when substances in the intestine pull water into the bowel
- Secretory diarrhea: Results from active secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestine
- Inflammatory diarrhea: Associated with intestinal inflammation from conditions like Crohn’s disease
This classification system helps healthcare providers determine the underlying diarrhea causes and select targeted treatments.
Common Diarrhea Causes: Food, Stress, Infections, and Illness
The triggers for hyperactive gut motility prove remarkably diverse. We can categorize the primary diarrhea causes into two main groups to better understand their origins.
1. Remote Diarrhea Causes: The Mind-Body Connection
Sometimes, the common causes of diarrhea originate far from the intestines themselves. These “sympathetic” reactions occur when other bodily systems or states disrupt digestive function.
Psychological Factors and the Gut-Brain Axis
A common question people ask is: Can stress cause diarrhea? The answer is definitively yes. The gut contains a vast network of neurons lining the digestive tract, earning it the nickname “second brain.” Intense emotions like anxiety, stress, or fear trigger the release of hormones that speed up gut motility, leading to sudden bowel urgency.
This gut-brain relationship demonstrates how the nervous system influences digestion directly. The powerful gut-brain axis provides a prime example of how remote factors become significant diarrhea causes.
Other Underlying Illnesses
Conditions seemingly unrelated to the gut can create a domino effect. For instance, teething may coincide with temporary digestive changes in infants, though infections or dietary factors often play concurrent roles. Similarly, systemic infections or chronic conditions can provoke digestive responses that manifest as diarrhea.
2. Direct Intestinal Irritants: Common Triggers
This represents the most frequent category of diarrhea causes, involving various irritants that directly aggravate the intestinal lining and prompt a rapid expulsion response.
Problematic Foods
Your diet stands as one of the most common causes of diarrhea in adults:
Overeating: Consuming too much food at once overwhelms the digestive system, forcing it to process a large volume quickly, which can lead to loose stools. Proper chewing plays a major role in preventing digestive overload by breaking down food adequately before it reaches the intestines.
Salty, Sugary, or Fatty Foods: Foods high in these components act as chemical stimulants. This explains why diarrhea after eating fatty foods represents such a common complaint. Many chronic digestive reactions stem from the long-term relationship between diet and disease.
Fermentable Foods: Certain foods that ferment easily in the gut—like some legumes and cruciferous vegetables—produce gas and irritating substances, leading to discomfort and diarrhea.
Medications and Toxins
This represents a significant category of diarrhea causes. Laxatives (purgatives) work by design to stimulate the bowels, and an overdose can cause severe diarrhea (hypercatharsis). Certain antibiotics, cancer drugs, and magnesium-containing antacids also serve as well-known culprits. Accidental ingestion of poisons triggers a severe defensive reaction as the body attempts rapid expulsion.
Internal Secretions and Issues
Sometimes, the body’s own fluids become diarrhea causes:
Excess Bile: An overproduction of bile, or bile that is more acrid than usual, irritates the intestines, leading to bile acid diarrhea symptoms. This occurs when the intestines cannot reabsorb bile acids properly.
Intestinal Gland Secretions: The watery consistency of diarrhea often originates from intestinal glands being stimulated to secrete fluid too rapidly—a process accelerated by various triggers.
Abscesses and Bleeding: In severe cases, the rupture of an abscess or bleeding from intestinal walls releases pus or blood into the stool, resulting in bloody diarrhea or melena (black, tarry stools). These symptoms always warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Malabsorption Issues
When the body fails to absorb nutrients properly, it leads to an accumulation of matter that draws water into the intestines, causing osmotic diarrhea. A classic example is celiac disease, where the body reacts to gluten and damages the intestinal villi, preventing proper absorption. This creates one of the chronic diarrhea causes that requires long-term dietary management.
Infections and Parasites
Intestinal worms, viruses (like norovirus), bacteria (like E. coli or Salmonella), and other pathogens represent major diarrhea causes. They inflame the intestinal lining and release toxins that trigger excessive fluid secretion. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diarrheal diseases remain a leading cause of child mortality globally, underscoring the critical nature of infectious diarrhea causes and the importance of prevention strategies.
How to Stop Diarrhea Fast: Effective Home Remedies and Treatment
Once you understand the potential diarrhea causes affecting you, the next step involves effective management. Here’s how to find relief and support your body’s recovery.
Prioritize Hydration
The most critical step involves replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. Drink plenty of water, clear broths, or oral rehydration solutions (ORS). Dehydration represents the most dangerous complication of diarrhea. Learn why proper hydration is essential for recovery in our comprehensive guide on the health benefits of drinking water.
Adopt the BRAT Diet
The BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) remains a proven remedy for acute diarrhea. These bland, binding foods are easy to digest and help firm up stools by adding bulk without irritating the intestinal lining. Other suitable options include boiled potatoes, plain crackers, and chicken broth.
Consider Over-the-Counter Medications
Anti-diarrheal medications like loperamide (Imodium) can provide short-term relief by slowing gut motility. Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) reduces inflammation and kills some bacteria.
Important safety note: Anti-diarrheal medications should not be used in cases of suspected infection with fever or bloody stools unless advised by a doctor. These medications can worsen certain bacterial infections by preventing the body from expelling harmful pathogens.
Introduce Probiotics
Taking probiotics during and after a bout of diarrhea helps replenish beneficial gut bacteria that may have been depleted, restoring balance and normal digestive function. Look for products containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains.
What to Avoid During Recovery
Certain foods and beverages worsen diarrhea symptoms:
- Dairy products (lactose can be difficult to digest)
- Caffeinated beverages (stimulate the intestines)
- Fatty or fried foods (slow digestion and irritate the gut)
- High-fiber foods (increase bowel movements)
- Alcohol (causes dehydration)
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Red Flags
While most acute diarrhea causes are benign and self-limiting, certain symptoms indicate a need for professional medical evaluation. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides guidelines on when to seek help, especially for persistent or travel-related cases.
Seek Medical Attention Immediately If You Experience:
- Signs of severe dehydration (dizziness, dark urine, extreme thirst, dry mouth, reduced urination)
- High fever over 102°F (39°C)
- Severe abdominal or rectal pain
- Diarrhea lasting more than 48 hours in adults (or 24 hours in children)
- Stools containing blood or pus, or that appear black and tarry
- Recent antibiotic use followed by severe diarrhea (possible C. difficile infection)
- Recent travel to areas with poor sanitation
- Compromised immune system
These warning signs may indicate serious underlying diarrhea causes that require medical intervention, including testing for specific pathogens or underlying digestive disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diarrhea Causes
How long does diarrhea from most common causes usually last?
Most acute cases, often caused by minor food-related triggers or viruses, last one to two days and resolve on their own without intervention. Viral gastroenteritis typically clears within 24-72 hours, while food poisoning may resolve in 12-48 hours depending on the pathogen involved.
Why do I have diarrhea but don’t feel sick?
You can experience diarrhea without other systemic symptoms. Common diarrhea causes in this scenario include mild food intolerance, stress-related digestive responses, or a minor infection that your immune system handles efficiently. Sugar alcohols (sorbitol, xylitol) and artificial sweeteners frequently cause this type of isolated diarrhea.
Are diarrhea causes different in children and adults?
Yes, what causes diarrhea in adults often differs from pediatric triggers. In children, diarrhea more commonly results from viral infections, and dehydration risk increases significantly due to smaller body size. Adults more frequently experience stress-related or diet-related diarrhea causes. Children also have less developed immune systems, making them more susceptible to infectious causes.
Can recurring diarrhea causes be a sign of something serious like cancer?
While persistent, unexplained changes in bowel habits can indicate colorectal cancer, this symptom appears far more commonly with less serious conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This is why consulting a doctor for proper diagnosis becomes essential if you experience chronic diarrhea lasting more than four weeks.
What should I eat when I have diarrhea?
Stick to bland, easy-to-digest foods like the BRAT diet, boiled potatoes, plain crackers, or chicken broth. Avoid dairy, spicy, fatty, or high-fiber foods until your digestion normalizes. Gradually reintroduce regular foods as symptoms improve, starting with simple proteins like baked chicken or fish.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Digestive Health
Understanding diarrhea causes empowers you to respond effectively when symptoms arise. Most cases resolve quickly with proper hydration, dietary adjustments, and rest. However, recognizing when symptoms indicate serious underlying conditions protects your long-term health.
If diarrhea becomes frequent, severe, or persistent, professional evaluation is essential to rule out underlying conditions and protect long-term digestive health. Healthcare providers can perform diagnostic testing, identify specific diarrhea causes, and develop targeted treatment plans.
By combining knowledge of common causes with practical treatment strategies, you can manage acute episodes effectively and maintain optimal digestive function for lasting wellness.
Author Bio: This article is written by the Pathway to a Healthy Lifestyle editorial team, focusing on evidence-informed digestive health, nutrition, and holistic wellbeing practices.
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult with qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment of persistent or severe diarrhea, especially in vulnerable populations like infants, elderly individuals, or those with compromised immune systems.

kl